—This Project is dedicated to my dear classmates from the 2017 class of the School of Architecture. —
—谨以此,先给我亲爱的建筑学院2017级同学。—
Along with the continuous development of contemporary game engines and XR technology, combined with the popularity of high-speed network online hardware and software, online exhibitions and virtual exhibition halls have become a new type of place different from traditional museums and display spaces, bringing a great expansion of traditional information display methods and viewing experiences in physical spaces. In the past two years, due to the demand for spatial isolation under sudden epidemics, major architecture universities at home and abroad have held exhibitions of relevant design works in online form, among which there is no lack of technical exploration and design innovation of various online virtual exhibition spaces.
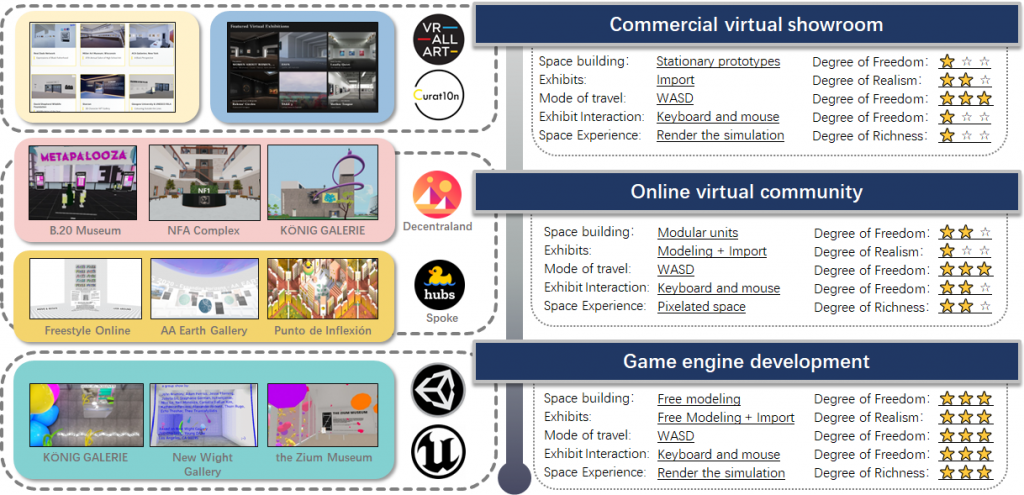
However, most of the existing online exhibitions are pre-determined by the exhibitors in terms of specific experience and display content and cannot provide the viewers with the freedom of viewing that they used to have in the physical exhibition space; and as a summary of teaching activities, most of the existing online exhibitions, which are mainly flat web pages, cannot provide students and teachers with an immersive experience. As the requirements of virtual exhibition halls for completely smooth all-round interactive exhibition functions and extremely realistic real-time 3D rendering display space rendering effects happen to be highly consistent with the goals pursued by game engines; and with the iterative upgrading of hardware and software equipment and other technologies, game engines such as Unreal Engine can optimize multiplayer real-time interaction rate through plug-ins such as Pixel Streaming, and XR technology based on this can simulate more realistic spatial environments.
Therefore, I hope to take the 2022 annual exhibition of the School of Architecture of Southeast University as an opportunity to design virtual exhibition buildings through the specific application of game engines and XR technology, so as to study the differences between virtual spaces and real scenes and the corresponding design methods.
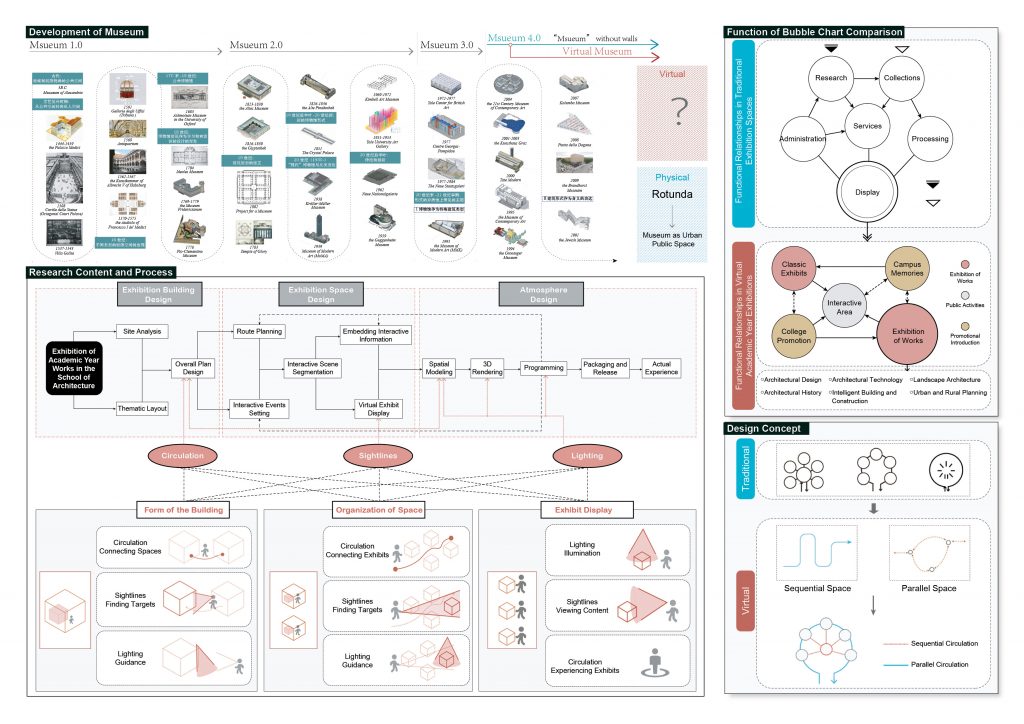
From the previous analysis, the significance of a three-dimensional virtual interaction space is twofold: firstly, in recreating the sensory experience of real-world environments, and secondly, in facilitating rapid indexing of information. Therefore, in my design, the virtual space is structured through computer system processing, while also integrating real-world flow lines with the interactive characteristics of virtual spaces for spatial design. Overall, the goal is to create a seamless flow and expand the dimensions of the virtual space through hyperlinks.
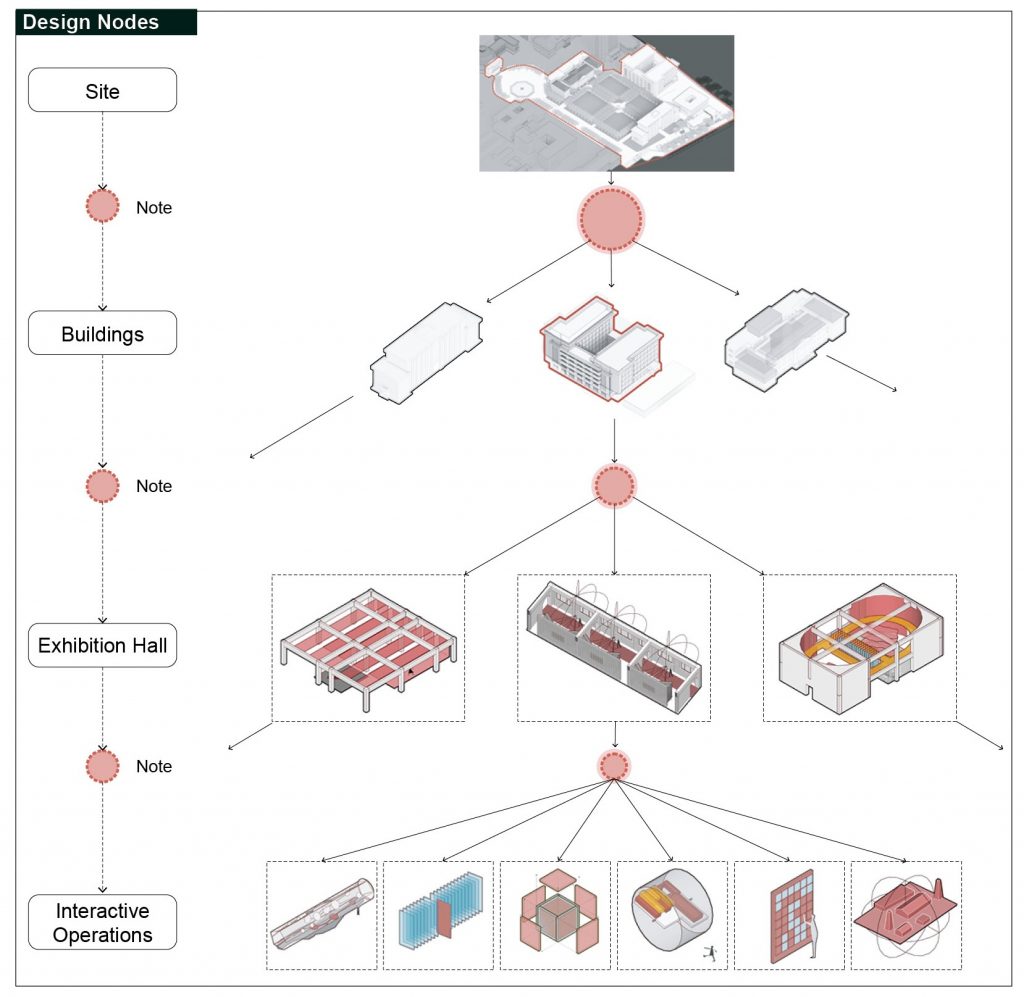
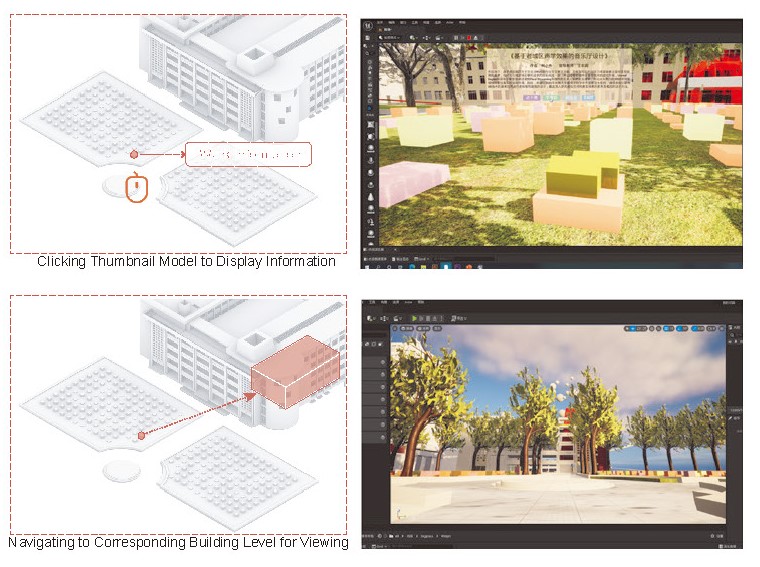
At the system architecture level, hyperlinks enable free navigation between the site, buildings, exhibition halls, and exhibits. In reality, the position of the large cauldron acts as the hub of the entire site’s enclosure. By clicking on the corresponding building portal, one can enter and view that building.
SPATIAL DESIGN
In spatial design, guiding visitor flow, creating a distinctive virtual space atmosphere, and presenting exhibits tailored to specific needs are key challenges. The expertise of architecture in spatial mastery can be applied to designing virtual environments, enhancing the experience by leveraging the unique features of virtual spaces to achieve a higher dimensional interaction.
■ Site Layout and Hub Space
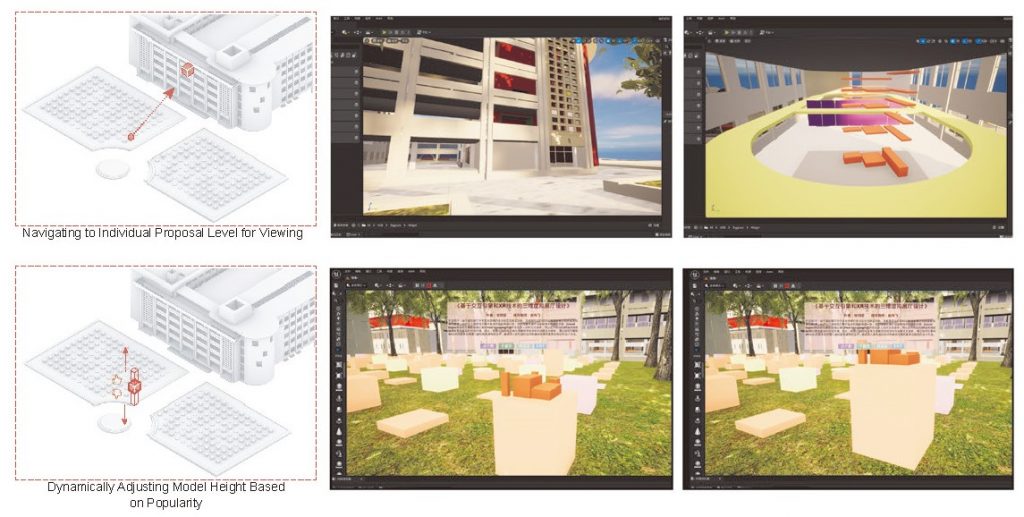
In reality, the position of the grand cauldron, serving as the central hub of the entire site, allows viewers to enter a building by clicking on the corresponding building entrance. Miniature models of each student’s graduation project are arrayed on the large lawn, with the height of each model reflecting the popularity of the respective project. Viewers can interact by liking or disliking the projects and click “Go Here” to directly view the specific work. The array of facade windows of the former engineering institute corresponds to the exhibition halls where individual projects are located, facilitating the transition between the site and the exhibition halls for the viewers.
■ Exhibition Hall Design
In the exhibition hall design section, traditional viewing experiences include walking inside the hall, selecting exhibits to view, and gaining an in-depth understanding of individual display elements. Therefore, I have sorted and corresponded the virtual space elements and the considerations of traditional exhibition design based on the scale of the virtual space, which is the level of digital information.
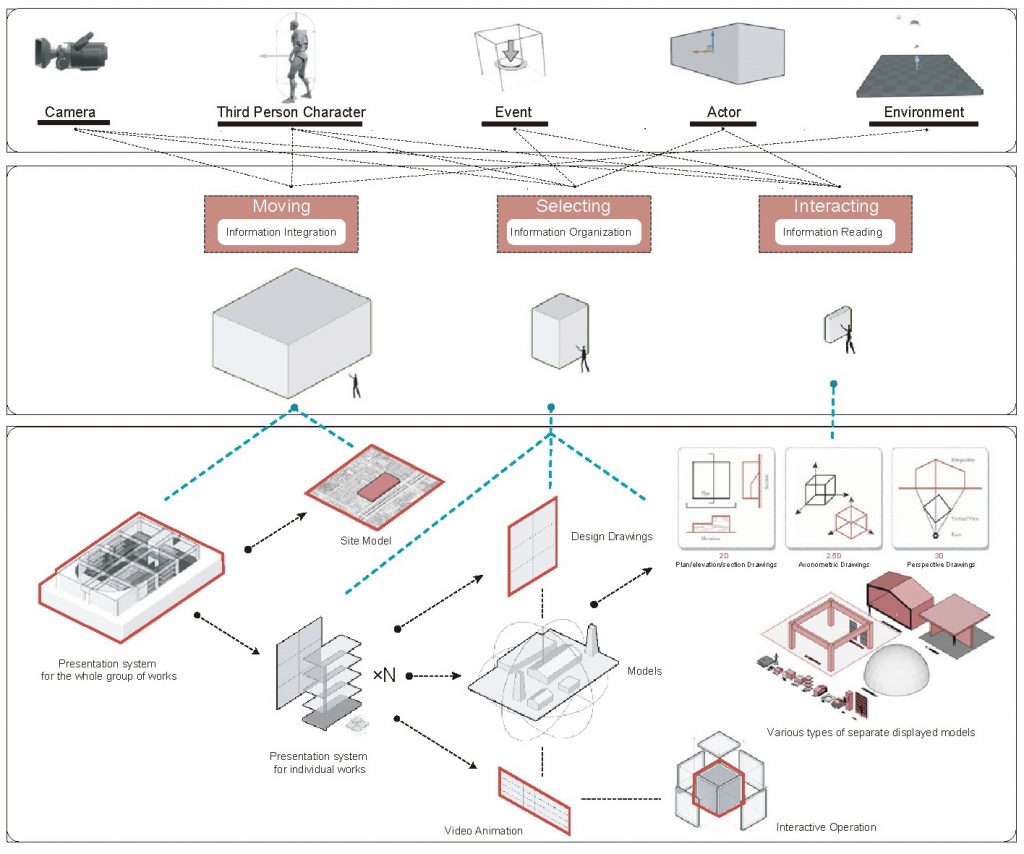
I have summarized the design content into four levels:
- Architectural space,
- Internal circulation,
- Exhibit organization,
- Interactive operations.
→ Virtual viewing and walking method
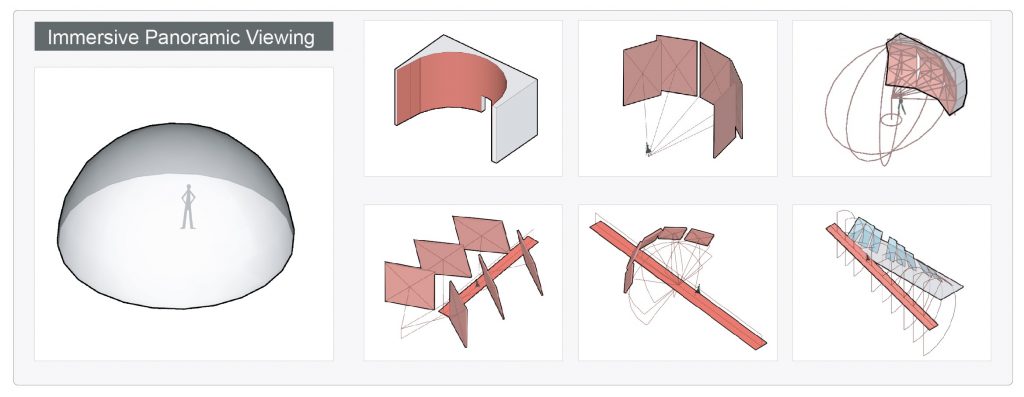
The attributes of the exhibition content and the modes of interaction also impact the virtual space. For example, the size and shape of the project site influence the operations within the virtual space and the selection of the exhibition hall location. Additionally, interactive methods such as spherical dome viewing affect the form and structure of the virtual environment.
→ Virtual approaching methods
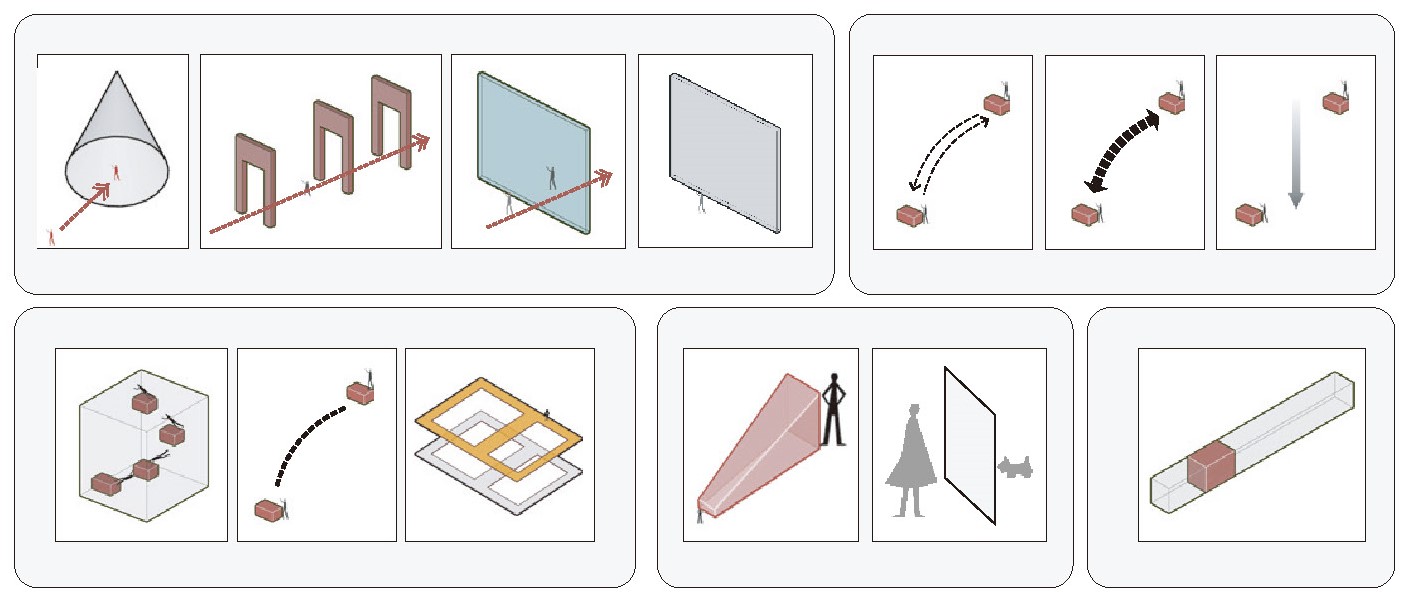
Regarding the walking methods within virtual spaces, in addition to the previously mentioned multi-point free-floating cylindrical spaces and hyperlinks at the architectural design level, the interaction between players and cameras in virtual spaces, as well as the transformation of the virtual player’s scale or role under specific trigger mechanisms, can all create experiences that go beyond the singular first-person perspective of real spaces. Additionally, virtual spaces can surpass the physical constraints and regulations of the real world by utilizing elements such as freely elevating platforms to achieve directional movement within the space.
→ Interaction with Architectural Works
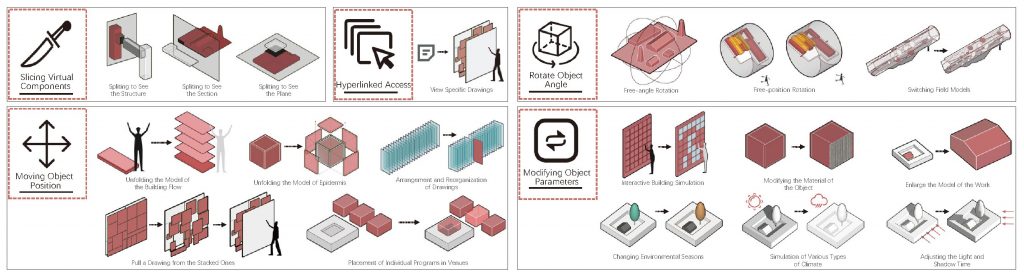
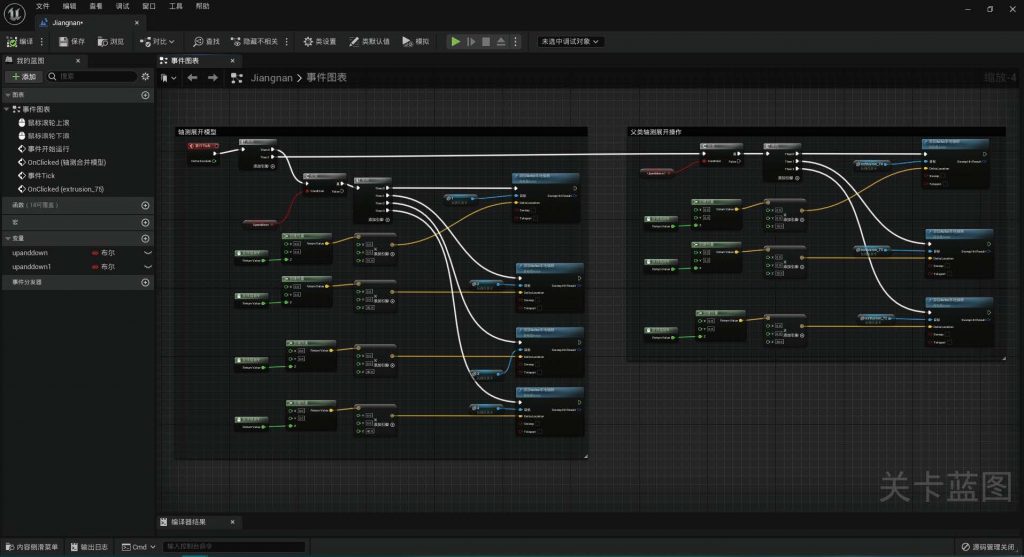
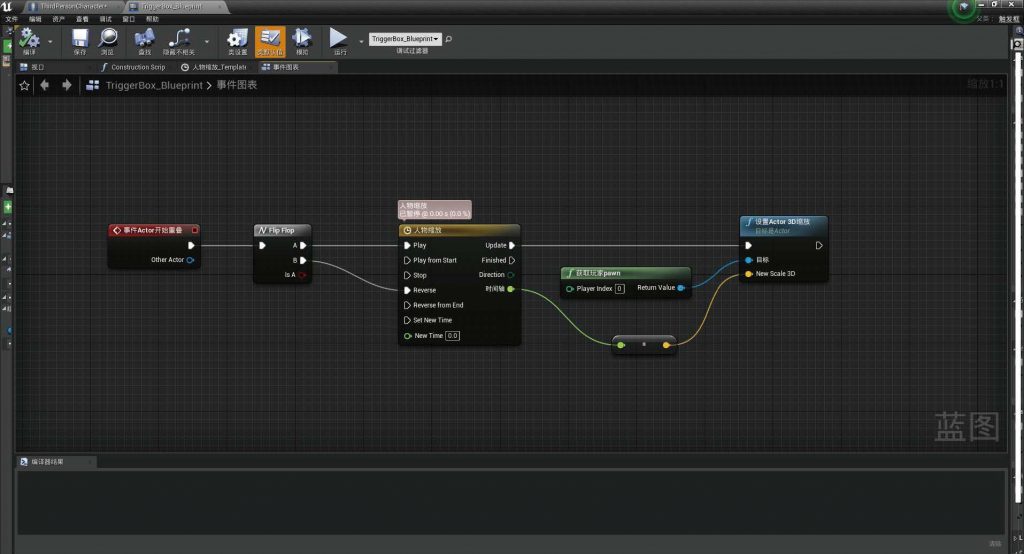
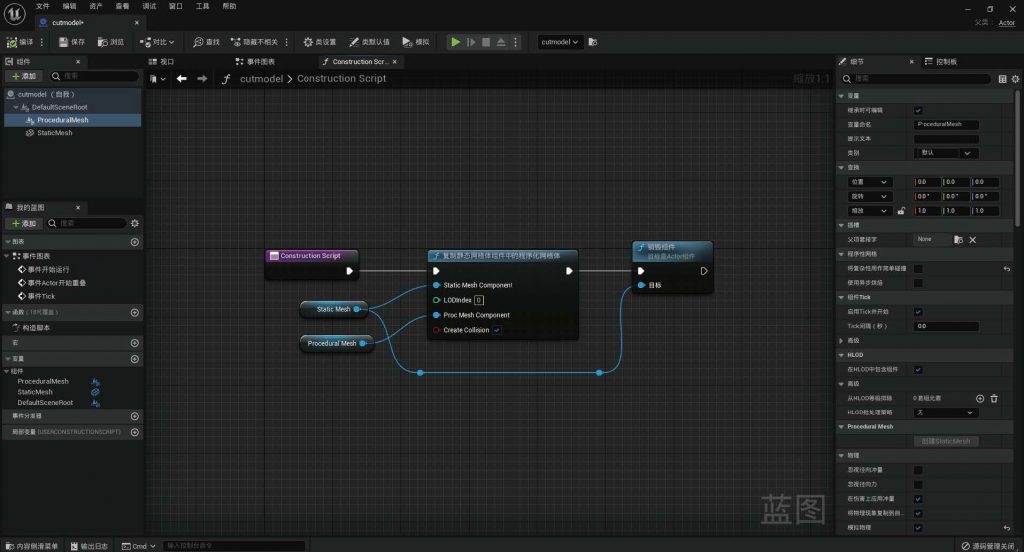
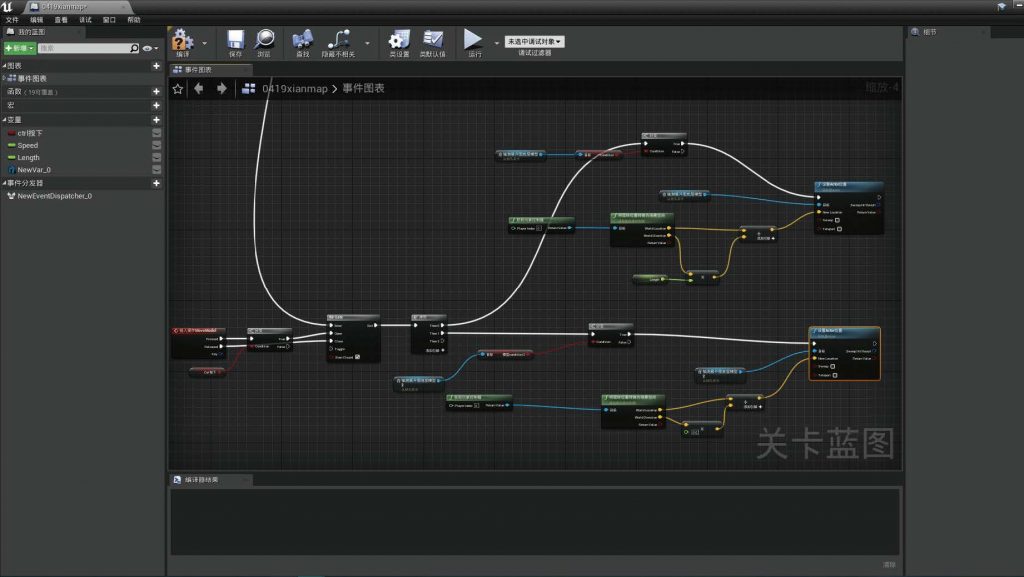
Based on typical virtual spaces, such as 3D scene games, and combined with the interactive operations simulated using Unreal Engine, my online exhibition interaction system can perform the aforementioned operations on virtual objects, namely virtual exhibits.
PROTOTYPE DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT
I conducted research on the themes, number of participants, collaboration methods, site forms, and sizes of each graduation project. Based on these aspects, I made preliminary designs and attempted to understand the exhibition requirements specific to each project.
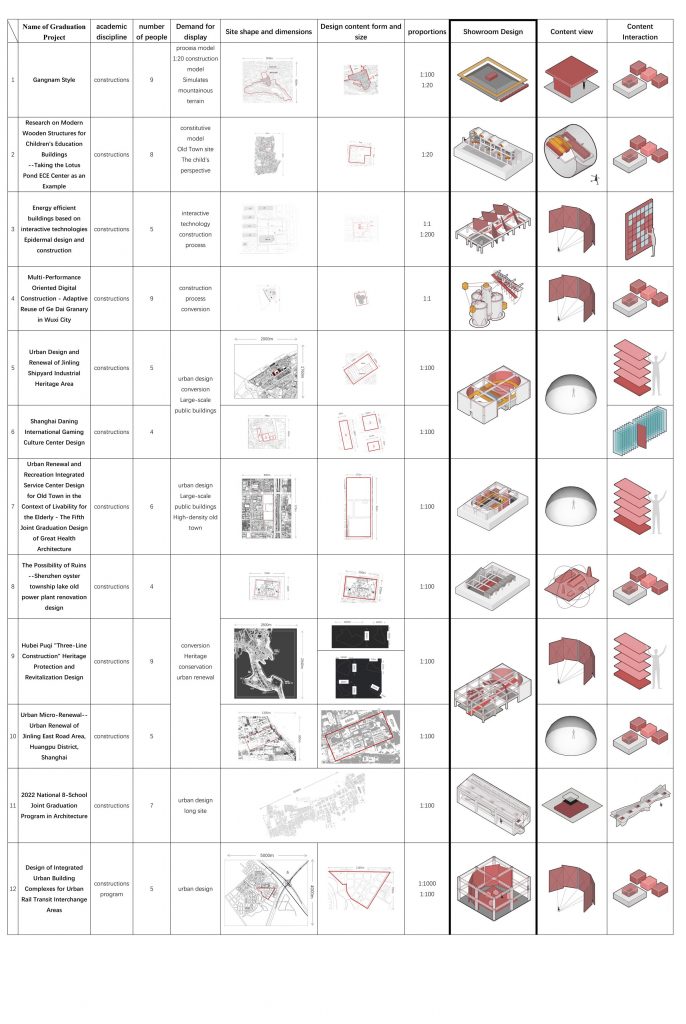
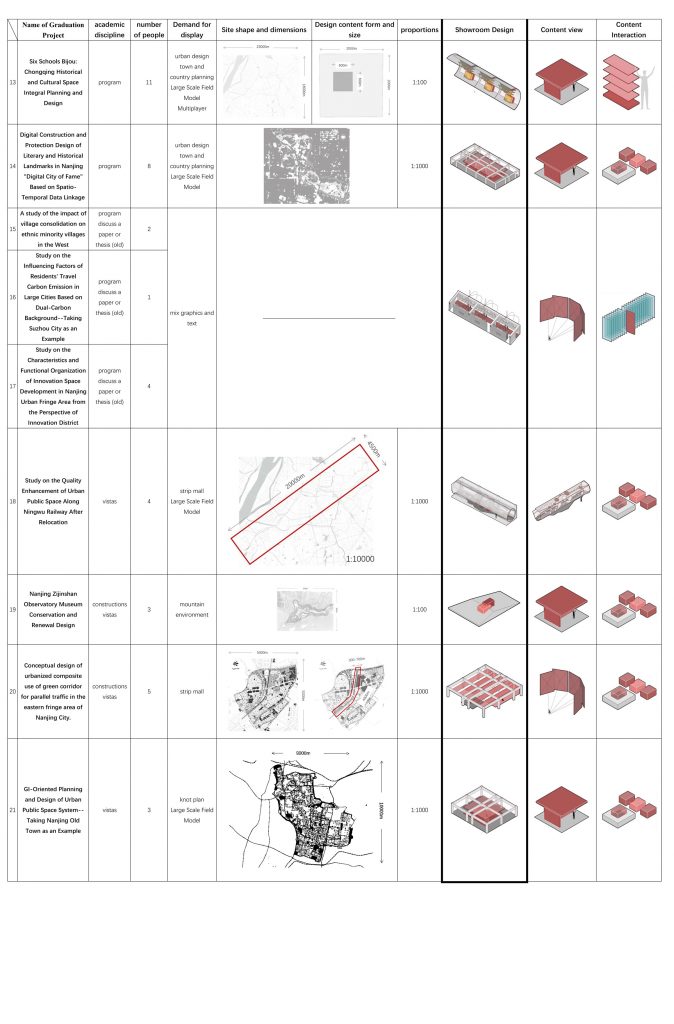
■ Organization of Display Rooms
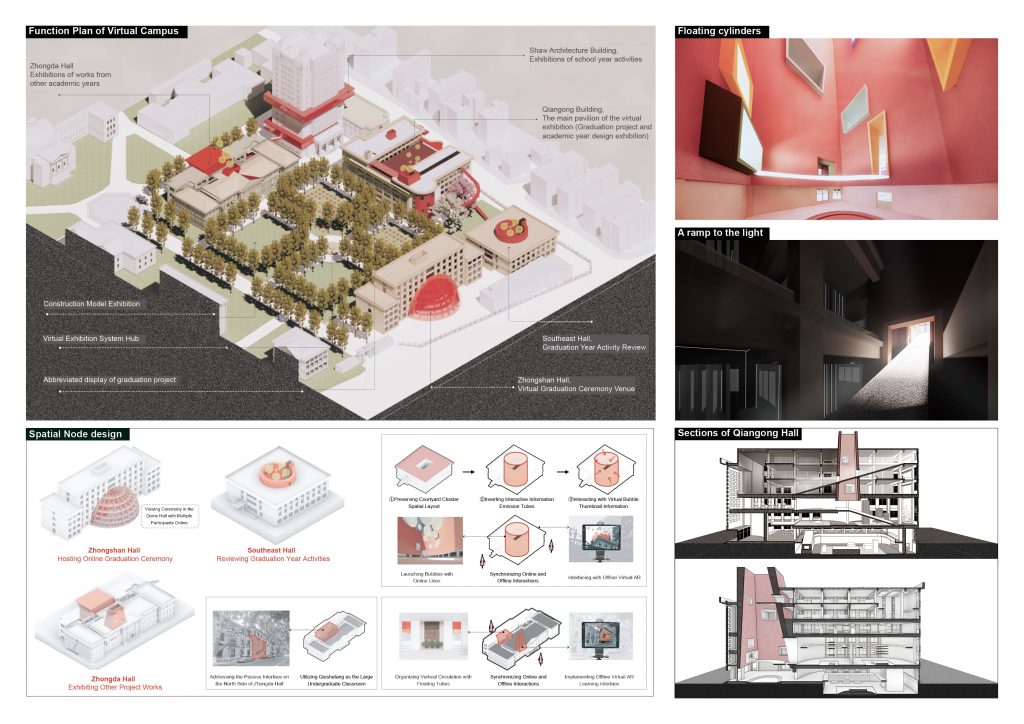
Additionally, I integrated the site environment and atmosphere of the architecture, as well as the characteristics of the space prototype of the former engineering institute, to arrange the functions and operate the spaces accordingly. I also incorporated the different scenes of spring, summer, autumn, and winter into the virtual exhibition architecture in a manner that transcends time and space.
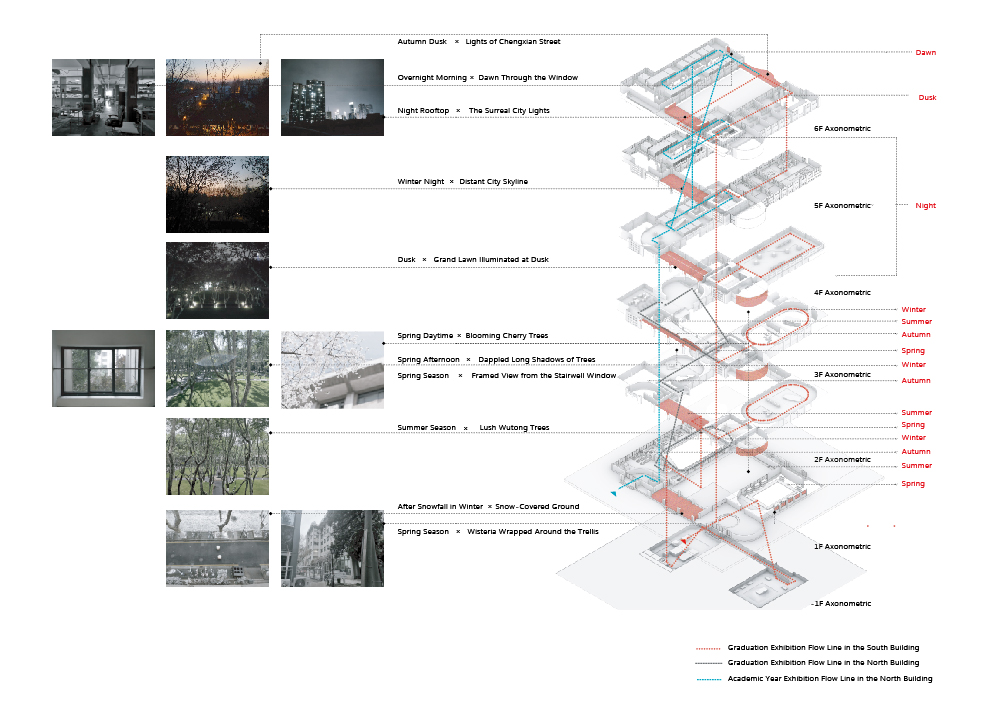
Prototype Development
I selected four representative exhibition halls to specifically explain the design concepts for individual project exhibition systems.
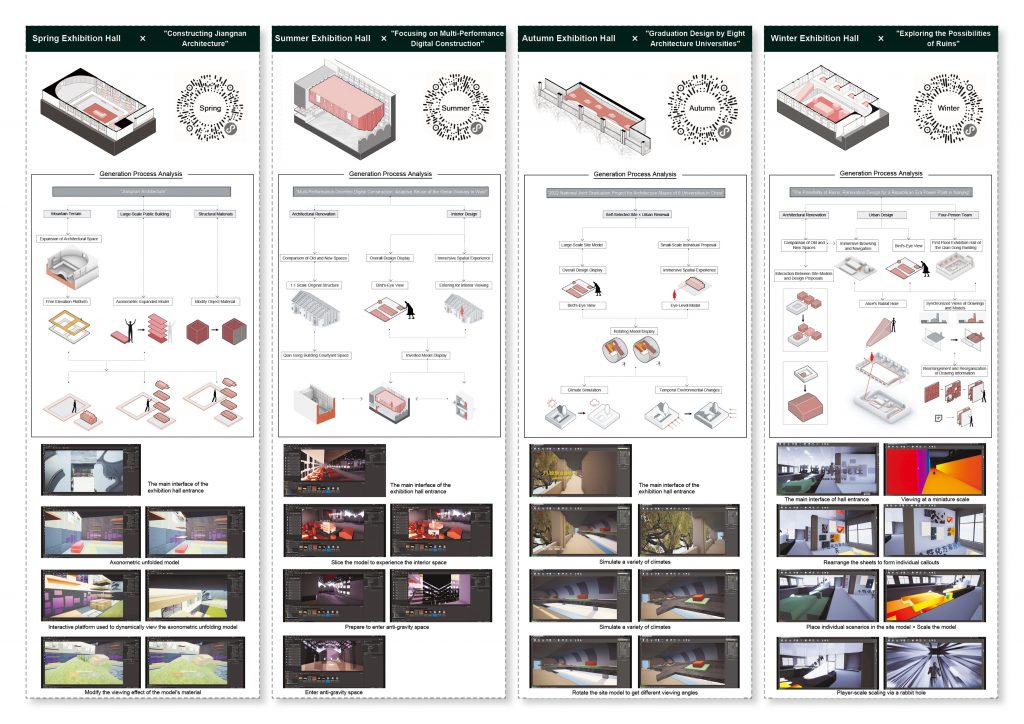
→ Spring hall
- Next to the blooming wisteria pergola in the South Building of the former engineering institute, the “Jiangnan Construction” project chooses the space on the first floor and the basement due to its special site environment—mountainous terrain. In virtual spaces, floors can be infinitely extended, so placing terrain like mountains, which significantly affect the height of the site model, in the basement and sinking it according to its height ensures that there is enough space above for virtual exhibition activities. For large public buildings, the rationality of spatial circulation is fundamental to determining the quality of the design. The “Jiangnan Construction” project, corresponding to a traditional large-scale axonometric model, would be difficult to see clearly at each level due to the fixed height of a normal person’s view. Therefore, combining the axonometric model with a freely elevating platform can achieve a more comprehensive and detailed understanding of the plan.
→ Summer Hall
- “Unaware of the sky in the water after being drunk, the full boat of star dreams presses down on the clear river.” The multi-performance-oriented digital construction project, focusing on the Wuxi Geli Granary area, involves large-scale urban design and experiments in digital construction using lightweight materials. Some students chose to design with the indoor space of a certain slope-roofed factory building. For the exhibition of such design works, it is necessary to display the entire architecture’s space and circulation design, as well as to present the construction details of lightweight materials and the spatial effects created at a 1:1 scale. The size of the slope-roofed factory building coincides with the atrium space of the former engineering institute, so this project is placed there, with the modified building object itself inverted and suspended in the air. This allows for an observation of the design content and its overall relationship with the original building when looking up and provides an immersive experience by entering the inverted building.
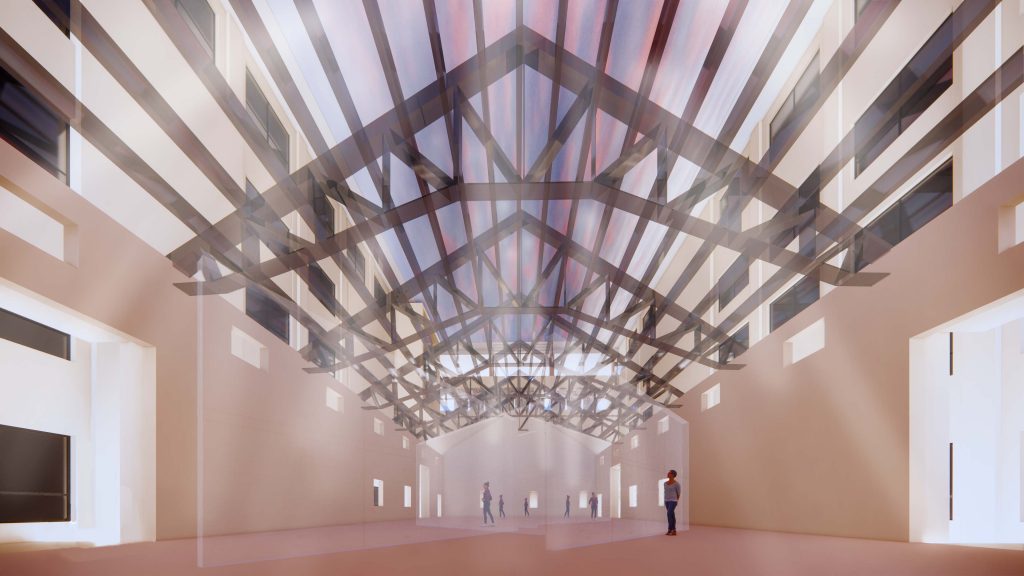
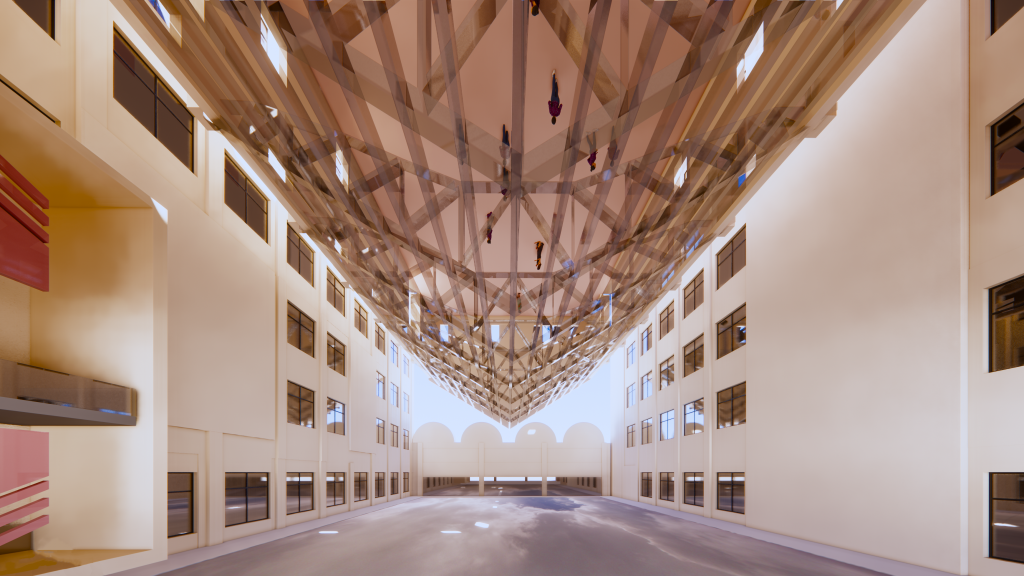


→ Autumn Hall
- The joint graduation design project of the eight architecture schools is set on Huaihai Road in Shanghai. The linear site matches the spatial form of the West Corridor of the former engineering institute, so it is arranged on the third-floor West Corridor, in line with the overall exhibition flow. This project requires students to explore potential design subjects within the site, resulting in different proposals with varying locations, collectively forming the overall urban renewal and design of Huaihai Road. In terms of interaction between viewers and the overall design outcomes, this exhibition hall provides a model viewing experience with preset model positions at eye level, offering a perspective view. Additionally, the rotation of the overall model offers other views, such as a bird’s-eye view. As the West Corridor is an excellent spot to view the large lawn and plane trees, the combination of the model’s rotation allows viewers to experience the passage of time in a dynamically changing environment.
→ Winter Hall
- The winter exhibition hall is located on the basement and first floor of the virtual North Building of the former engineering institute, used for the “Possibilities of Ruins: Renovation Design of a Republic of China-era Power Plant in Nanjing” project. For this project, which involves urban-scale renovation design, traditional exhibitions cannot switch to compare the spatial effects before and after the renovation. A few key renderings also cannot fully showcase the continuous dynamic spatial experience in large-scale site designs. However, the virtual space can innovate the organization of various exhibits and the internal circulation of the exhibition hall through interactive operations, enriching the ways of understanding and viewing the exhibits.
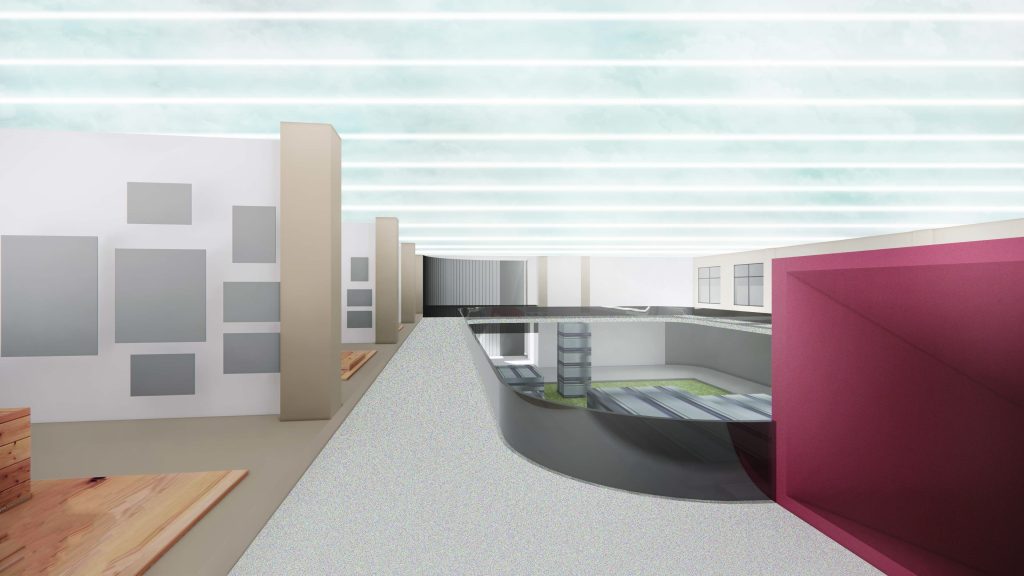
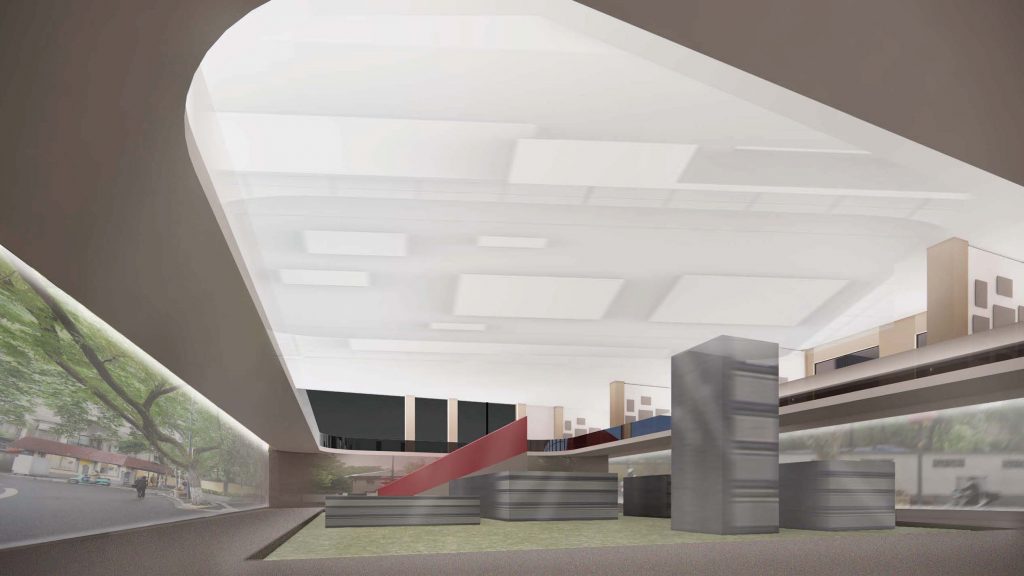


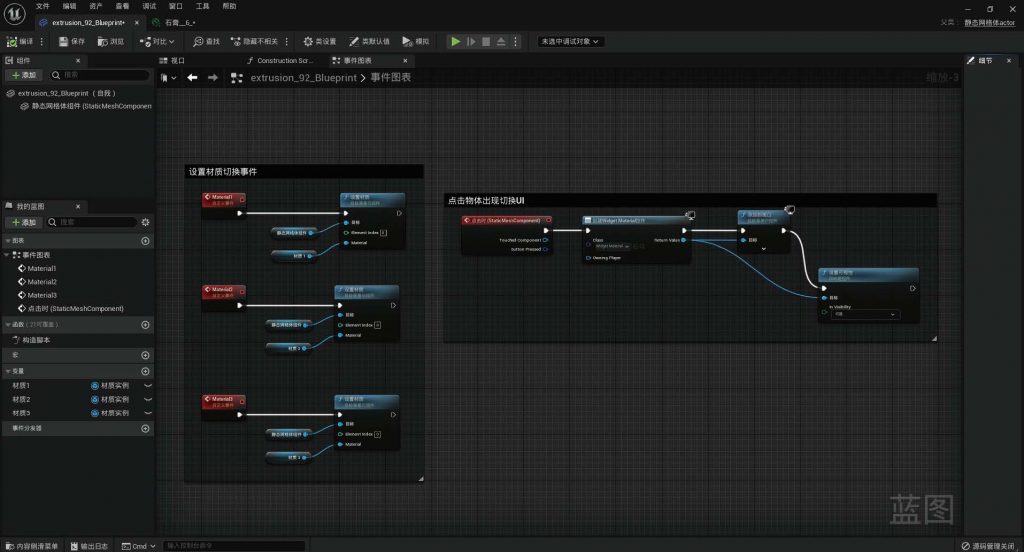
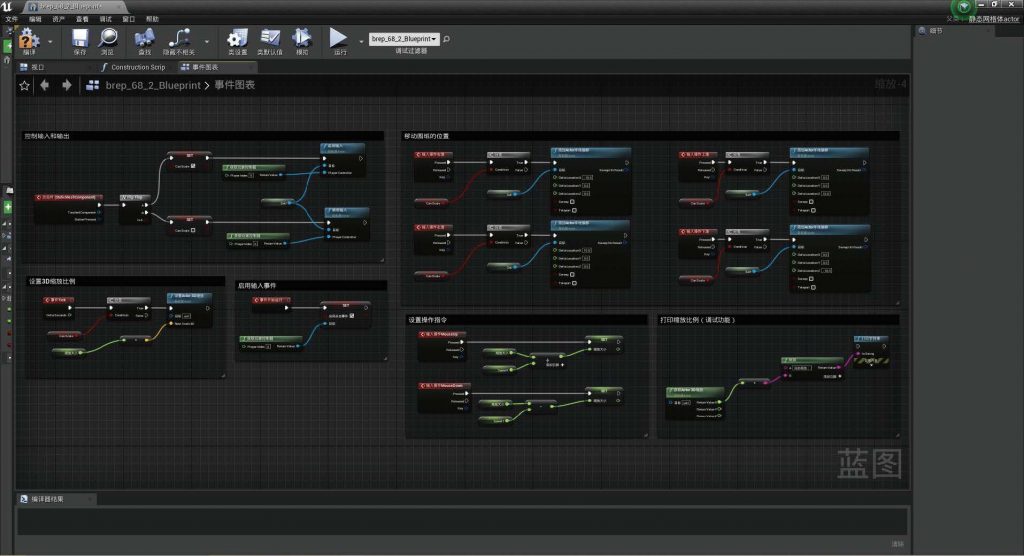
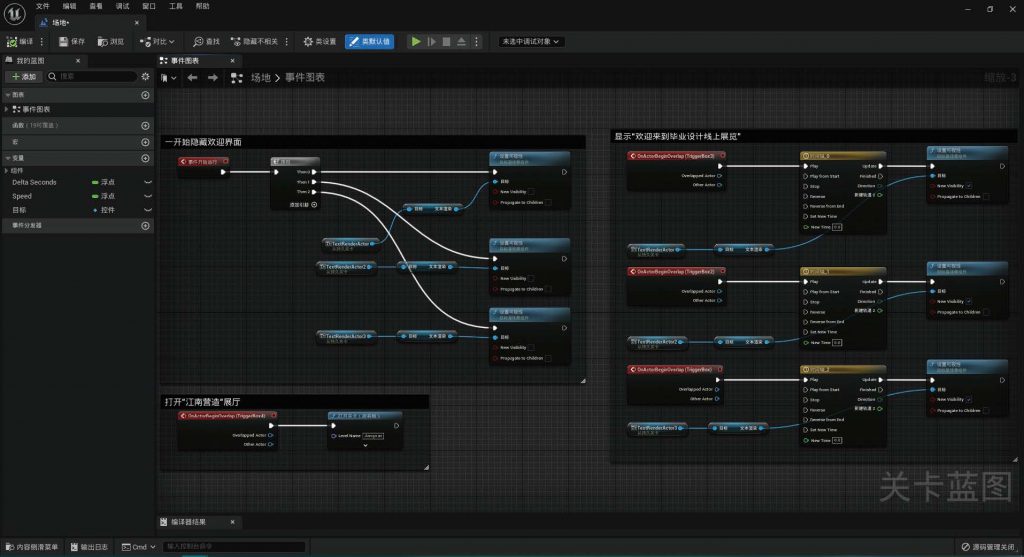
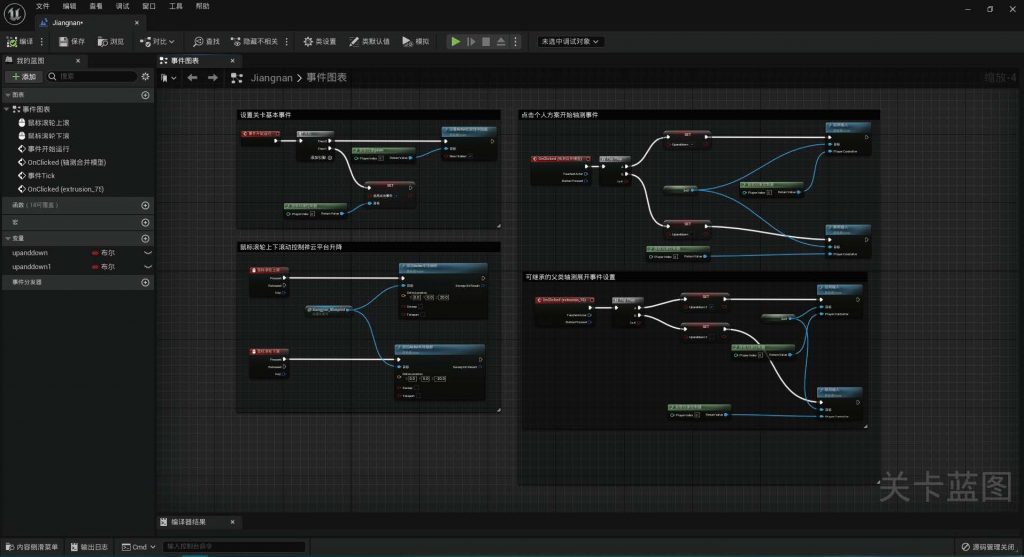
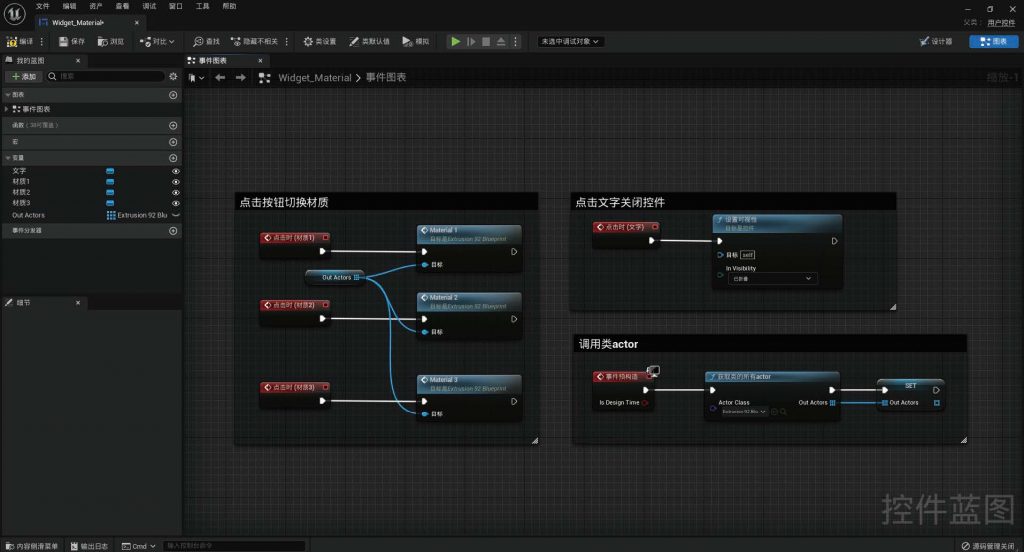
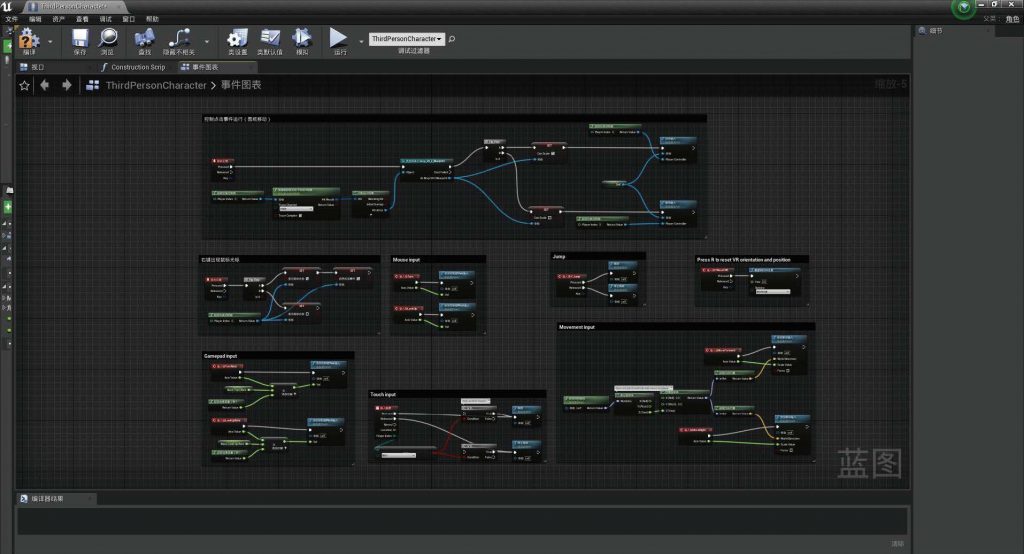
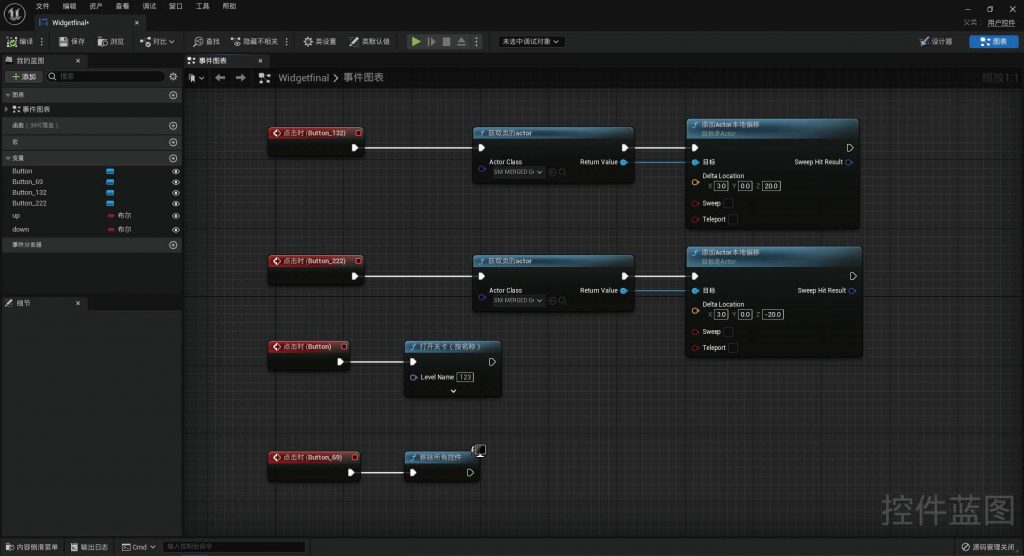
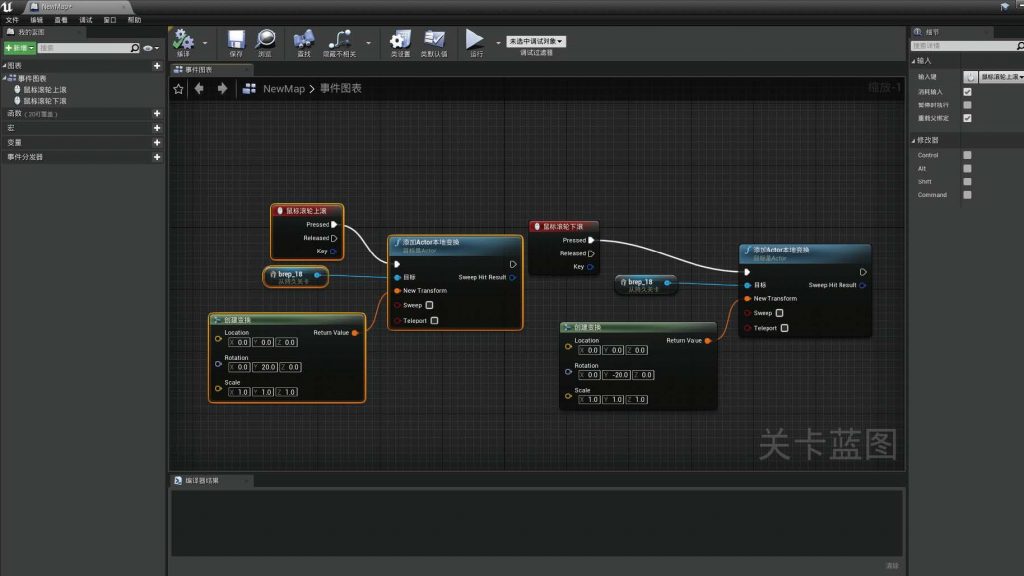
BLUEPRINT IN UNREAL ENGINE
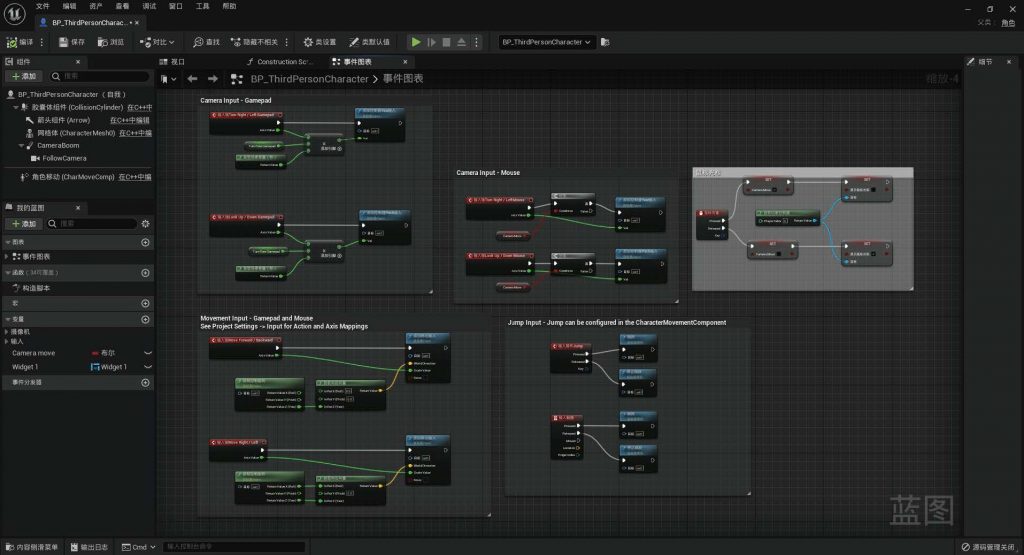
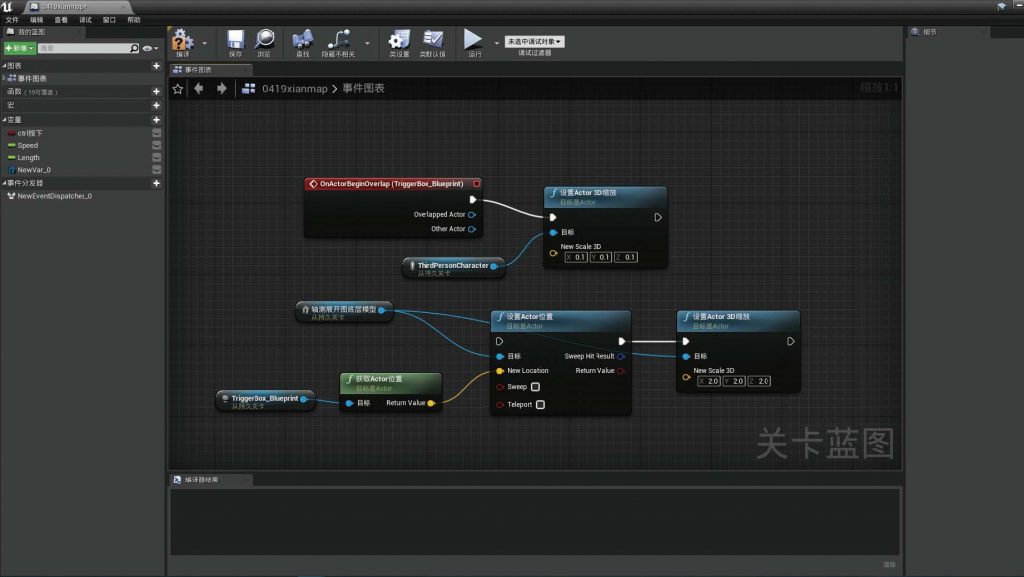
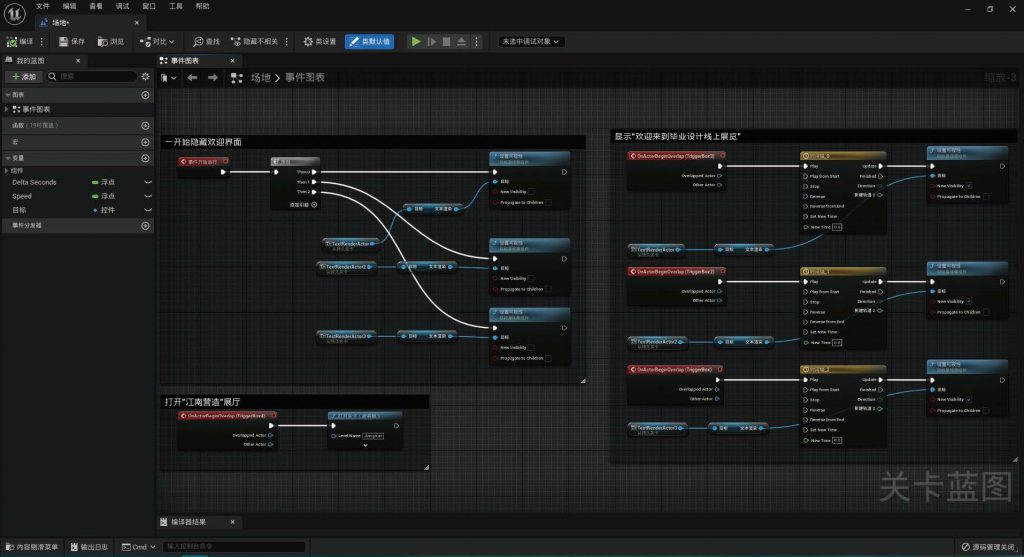
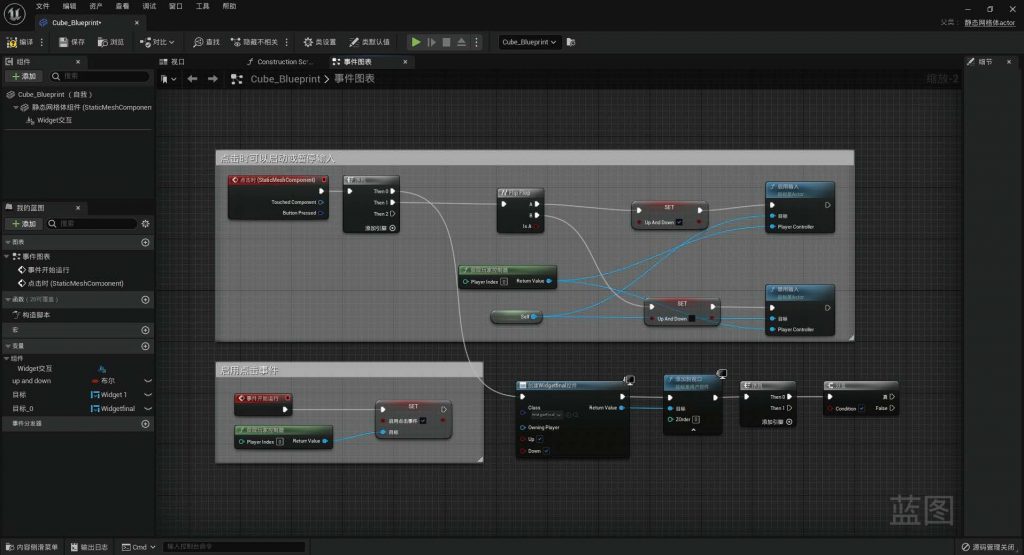
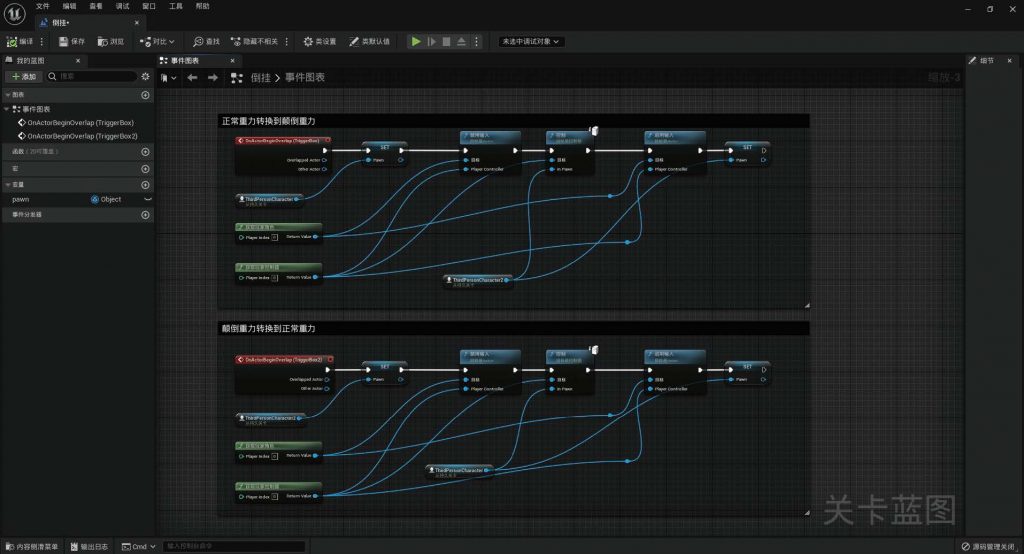
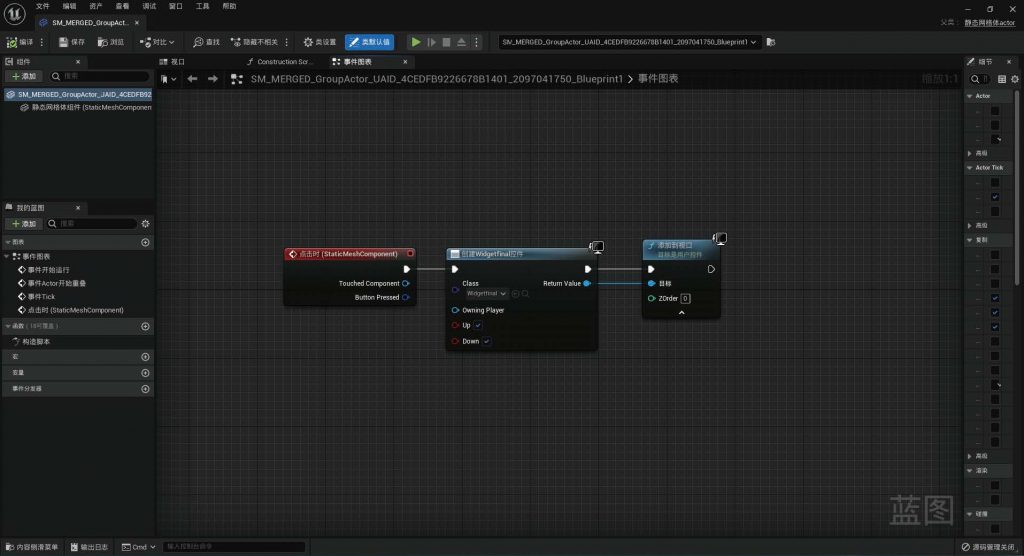
-scaled.jpg)
Leave a Reply